The IL-4/IL-13 signaling pathways include IL13RA1, IL13RA2, and IL4R subunits, which are IL-13 receptors. They are connected to the pathophysiology and advancement of therapeutics for asthma, cancer and allergic diseases. IL13RA2 is being clinically tested as a possible cancer vaccination and CAR-T treatment target as a glioma-specific cell-surface epitope.
Functionally, there are two categories of IL-13 receptors: shared and private. IL13RA1 and IL4R make up the common IL-13 receptor. Additionally, IL-13 may bind to the exclusive IL-13 receptor IL13RA2. The main IL13-binding component of the IL-13 receptors is IL13RA1. By functioning as a decoy receptor with a greater affinity, IL13RA2 may inhibit IL-13-induced STAT6 activation.
By triggering AP-1 signaling and the synthesis of TGF beta, TNF-alpha and IL-13 signaling may cause the overexpression of IL-13RA2, which can have pro-fibrotic consequences. In order to facilitate IL-4 signaling, IL-4R can additionally complex with the common gamma chain (γc/IL2RG).
To support the study of IL-13 Receptors in understanding the immune response to neoplastic and inflammatory illnesses, Sino Biological has created a variety of high-quality proteins, antibodies, genes, lysate, and qPCR primer pairs.
Features of recombinant IL-13 receptors
- High activity, high purity
- Various species: Human, mouse, canine, rat, and cynomolgus
Features of antibodies targeting IL-13 receptors
- Rabbit MAb and PAb, mouse MAb
- Multiple applications: Validated in neutralization, ELISA, WB, IF, and ICC
Sino Biological has created high-quality recombinant IL-13 receptor proteins from a variety of species, including cynomolgus, canine, human, mouse, and rat.
Features IL-13 and receptors
Human IL-13 protein
Cat#: 10369-HNAC
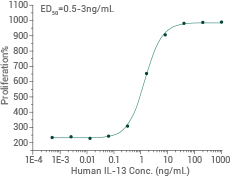
Cell proliferation assay using TF1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Cynomolgus IL4R protein
Cat#: 90897-C02H
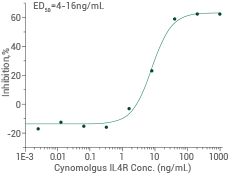
Ability to inhibit IL-4 dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erthroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
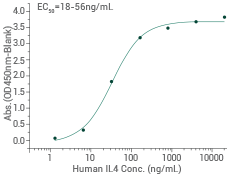
Immobilized Human IL4 (Cat#: 11846-HNAE) can bind Cynomolgus IL4R Protein. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Cynomolgus IL13RA1 protein
Cat#: 90864-C08H
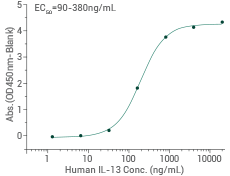
Immobilized Human IL-13 Protein (Cat#: 10369-H01H) can bind Cynomolgus IL13RA1 Protein. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Mouse IL13RA2 protein
Cat#: 50061-M38H
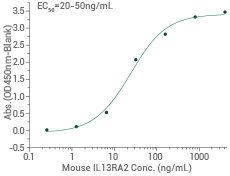
Immobilized mouse IL13RA2 can bind IL13/Biotin (Cat#: 10369-HNAC). Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
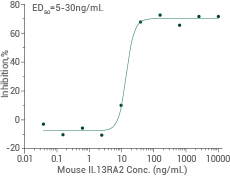
Ability to inhibit mouse IL13-dependent proliferation of TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Other related proteins
- IL-4
- IL2RG
- TNF-alpha
- TGF beta
- STAT6
- STAT1
Antibodies for IL-13 receptors
More than 50 different types of IL-13 receptor-targeting antibodies have been created by Sino Biological and may be used for neutralization, ELISA, WB, IF, and ICC.
Anti-IL-4R neutralizing rabbit MAb
Cat#: 10402-R001
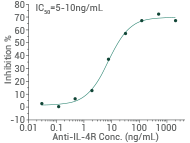
Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Human IL4 is neutralized by increasing concentrations of Human IL4R Monoclonal Antibody. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anti-IL13RA1 rabbit Mab
Cat#: 310231-T08
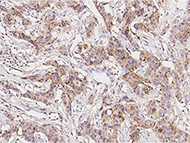
Immunochemical staining of human IL13RA1 in human breast carcinoma. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anti-IL13RA2 rabbit Mab
Cat#: 10350-R018-A
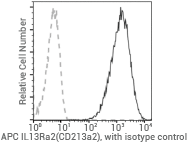
Flow cytometric analysis of Human IL13RA2 expression on A375 cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
More antibodies targeting IL-13 receptors
- Anti-IL4R
- Anti-IL13RA1
- Anti-IL13RA2